INTRODUCTION
In recent decades, bioimaging,[1] such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI),[2-4] optical imaging,[5-7] etc., has been an essential approach for pathological analysis as well as biomedical research, which enabled the detection of biological processes in vivo or in vitro.[8-12] As one of the most widely used bioimaging techniques, fluorescence imaging could provide information to reflect the dynamic reaction process of specific biomolecules.[13] Compared with other microscopies such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM),[14-16] atomic force microscopy (AFM),[17-20] and transmission electron microscopy (TEM),[21-24] fluorescence imaging could provide real-time in situ images for disease theranostics.[25] For instance, Scocchi[26] utilized dipyrrometheneboron difluoride (BODIPY) to label polymyxin B to visualize its interaction to bacteria, which could help study the antibacterial mechanism. However, organic fluorophores often suffer from high susceptibility to photobleaching and limited specificity.[27,28]
Polymer vesicles, also known as polymersomes, have been widely applied in biomedical field due to their hollow nanostructure and compartmentalized domains with diverse functionalities.[29-38] Amphiphilic homopolymers,[39] polypeptides,[40] glycopeptides[41] and other block copolymer[42] have been developed for preparing functional polymer vesicles. Among them, antimicrobial peptides/polypeptides based vesicles were synthesized with broad-spectrum antibacterial activity to meet the challenge of antimicrobial resistance.[43,44] For example, antimicrobial peptides/polypeptides based vesicles exhibited enhanced antibacterial activity in contrast to peptides/polypeptides alone due to the increased local positive charges and enhanced stability.[45-48] Besides antibacterial activities, polymer vesicles have also been endowed with fluorescence property by encapsulating organic dyes.[38,49] For example, Andreas encapsulated fluorescent dyes into polymer vesicles to monitor membrane transport of peptides in real time.[49] However, the unavoidable leakage and possible cytotoxicity of organic dyes could be a problem for in situ real-time imaging.[38,50-53] Therefore, it would be of great value to integrate intrinsic fluorescence and antibacterial activity together into polypeptide vesicles.
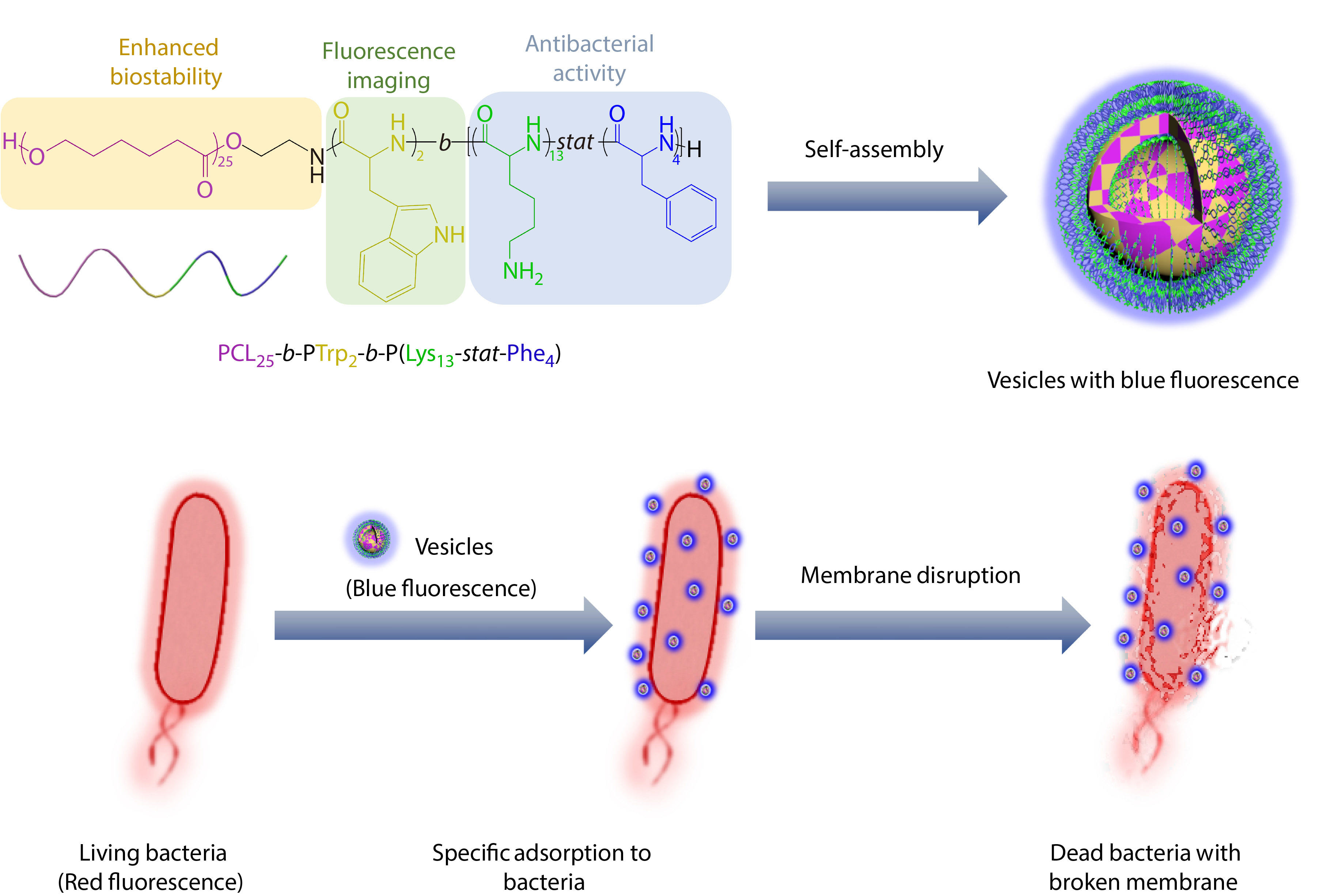
Herein, we designed and synthesized a polypeptide-based vesicle with antibacterial activity and intrinsic blue fluorescence (Scheme 1). At first, through ring-opening polymerization of N-carboxyanhydrides (NCAs) with poly(ε-caprolactone)-NH2 (PCL-NH2) as initiator, we synthesized a triblock copolymer, poly(ε-caprolactone)-block-poly(tryptophan)-block-poly(lysine-stat-phenylalanine) [PCL25-b-PTrp2-b-P(Lys13-stat-Phe4)], which could assemble into vesicles with intrinsic blue fluorescence. The biocompatible and biodegradable PCL chains form the vesicle membrane, and the antibacterial polypeptides [P(Lys-stat-Phe)] coronas provide positive charges and hydrophobic effects. In addition, the polymerization of aromatic amino acids and formation of hydrogen bonds during self-assembly would induce the delocalization of electrons for fluorescence red shift to visible range,[54-56] which could be applied to visualize the antibacterial process against planktonic bacteria. Through utilizing the intrinsic fluorescence of vesicles, real-time visualization of interactions between vesicles and bacteria was conducted using confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) to validate the specific adhesion of vesicle towards bacteria and the bacterial death through membrane disruption.
EXPERIMENTAL
Materials
N-ε-benzyloxycarbonyl-L-lysine, L-phenylalanine, hexane, L-tryptophan, α-pinene, triphosgene, ε-caprolactone, toluene, N-Boc-ethanolamine, methanol, tetrahydrofuran (THF), dichloromethane, trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), sodium sulfate anhydrous, hydrogen bromide (30% in acetic acid), acetone, and N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) were purchased from Aladdin. THF was dried by reflux for 1 day in the presence of potassium hydroxide and sodium strips. Stannous 2-ethylhexanoate (Sn(Oct)2) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. CDCl3 and DMSO-d6 were purchased from J&K Scientific Ltd. Gram-negative bacterium (E. coli. ATCC35218) and Gram-positive bacterium (S. aureus, ATCC29213) were purchased from Nanjing Bianzhen Biological Technology Co., Ltd. Other chemicals were used without further purification unless otherwise specified.
Synthesis of Copolymers
Synthesis of Z-Lys-NCA monomer
The synthetic routes of NCAs are shown in Fig. S1 in the electronic supplementary information (ESI). N-ε-benzyloxycarbonyl-L-lysine (5.00 g, 34.5 mmol), triphosgene (3.80 g, 12.8 mmol) and α-pinene (5.00 mL, 31.6 mmol) were dissolved in THF (100 mL) in a round-bottom flask with a magnetic flea. The reaction solution was stirred and refluxed at 55 °C in an oil bath for 4 h. The mixture would gradually turn clear in 4 h. Then the reaction was cooled down to room temperature. The mixture was precipitated in hexane (600 mL) with fast stirring for three times. The obtained product could be used after 24 h of drying in vacuum. The 1H-NMR spectrum is shown in Fig. S2 in ESI. Yield: ~90%.
Synthesis of Phe-NCA monomer
L-phenylalanine (10.0 g, 58.5 mmol), triphosgene (12.0 g, 40.4 mmol) and α-pinene (10.0 mL, 63.2 mmol) were dissolved in THF (150.0 mL) in a round-bottom flask with a magnetic flea. The reaction solution was stirred and refluxed at 55 °C in an oil bath for 4 h. The mixture would turn gradually clear in 4 h. The reaction was allowed to cool to room temperature. Then 100 mL of THF was removed by rotary evaporator under vacuum. The mixture was precipitated in hexane (600 mL) with fast stirring for three times. The obtained product could be used after 24 h of drying in vacuum. The 1H-NMR spectrum is shown in Fig. S3 in ESI. Yield: ~83%.
Synthesis of Trp-NCA monomer
L-tryptophan (5.00 g, 24.3 mmol), triphosgene (4.00 g, 13.5 mmol) and α-pinene (10.0 mL, 63.2 mmol) were dissolved in anhydrous THF (150 mL) in a two-neck round-bottom flask with a magnetic flea. Argon gas was introduced into the flask for 30 min to remove oxygen. Then the suspension was stirred and refluxed at 55 °C in an oil bath under argon protection for 4 h. The mixture would gradually turn clear in 4 h. The reaction was allowed to cool to room temperature. The reaction solution was quickly poured into hexane (900 mL) and then recrystallized at –20 °C for 12 h. A white crystal was obtained by filtrating the reaction solution. The obtained product could be used after 24 h of drying in vacuum. All operations need to be protected from light. The 1H-NMR spectrum is shown in Fig. S4 in ESI. Yield: ~78%.
Synthesis of PCL-NH-Boc
ε-Caprolactone (30.00 g, 232.8 mmol) was dissolved in toluene (600 mL) in a round-bottom flask with a magnetic flea. Toluene and water (40.0 mL) were removed by azeotropic in an oil bath at 140 °C. The mixture was cooled down to room temperature. N-Boc-ethanolamine (1.30 g, 8.06 mmol) was added into the flask. Argon gas was introduced into the flask for 20 min to remove oxygen. Sn(Oct)2 (0.019 g, 0.044 mmol) was added into the flask. Argon gas was introduced into the flask for 10 min to remove oxygen. The reaction solution was stirred and refluxed at 110 °C in an oil bath under argon protection for 48 h. The toluene was removed by rotary evaporator under vacuum. The mixture was dissolved in dichloromethane (20.0 mL) and was precipitated in methanol (200 mL) at –4 °C with fast stirring for three times. The obtained product could be used after 24 h of drying in vacuum. The 1H-NMR spectrum and SEC trace are shown in Figs. S5 and S6 in ESI. Yield: ~84%.
Synthesis of PCL-NH2
PCL-NH-Boc (7.00 g) was dissolved in dichloromethane (20.0 mL) in a round-bottom flask with a magnetic flea. After all the PCL-NH-Boc was dissolved, TFA (20.0 mL) was added into the flask. The reaction solution was stirred at room temperature for 4 h. The dichloromethane was removed by rotary evaporator under vacuum. The mixture was washed with saturated NaHCO3 (2×200 mL) and deionized water (2×200 mL) successively. The organic phase was dissolved in dichloromethane (80.0 mL) and was dried over anhydrous Na2SO4 and then the dichloromethane was removed via rotary evaporator. The resulting product could be used after 24 h of drying in vacuum. The 1H-NMR spectrum is shown in Fig. S7 in ESI. Yield: ~56%.
Synthesis of PCL-b-PTrp-b-P[(Z-Lys)-stat-Phe]
PCL-NH2 (1.803 g) and L-Trp-NCA (1.046 g) were dissolved in anhydrous DMF (20.0 mL) in a round-bottom flask with a magnetic flea. The reaction solution was stirred in vacuum at room temperature for 48 h. Then Z-Lys-NCA (3.706 g) and Phe-NCA (1.603 g) were added into the flask.
The reaction solution was stirred in vacuum at room temperature for 48 h. The mixture was obtained by dialysis in water. Finally, the product was obtained by freeze-drying for 48 h. The 1H-NMR spectra are shown in Figs. S8 and S9 in ESI. Yield: ~67%.
Synthesis of PCL-b-PTrp-b-P(Lys-stat-Phe)
PCL25-b-PTrp2-b-P[(Z-Lys)13-stat-Phe4)] (1.00 g) was dissolved in HBr (10.0 mL, 30% in acetic acid) in a round-bottom flask with a magnetic flea. The reaction solution was stirred at room temperature for 4 h. The mixture was precipitated in acetone (250 mL) with fast stirring once. The mixture was centrifuged for 3 min at 8000 r/min and the solid at the bottom of centrifuge tube was dialyzed in water for 48 h. Finally, the product was obtained by freeze-drying for 48 h. The 1H-NMR spectrum is shown in Fig. S10 in ESI. Yield: ~27%.
Self-assembly of Copolymers
PCL25-b-PTrp2-b-P(Lys13-stat-Phe4) (10.0 mg) was dissolved in DMF (2.0 mL). One drop of TFA was added to break the hydrogen bonding to ensure the complete dissolution of the polymer. Then, deionized water (6.0 mL) was added dropwise into the solution by a burette with vigorous stirring for 10 min. After stirring for another 30 min, the dispersion was transferred into a dialysis tube and dialyzed against deionized water for 48 h to remove DMF and TFA.
Characterizations
The molecular weight and polydispersity of PCL25-b-PTrp2-b-P(Lys13-stat-Phe4) copolymer were determined by a size exclusion chromatography (SEC) performed at 35 °C using a Waters Breeze 1525 GPC analysis system with two PL mix-D columns. HPLC grade THF was used as an eluent with a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min at 35 °C and the samples were calibrated with PEO standard samples. The polymer (10.0 mg) was dissolved in 2.0 mL of DMF and filtered before analysis. Differences for the molecular weight between SEC and 1H-NMR results can be ascribed to calibration with PEO standard samples of SEC.
The 1H-NMR spectra were recorded using a Bruker AV 400 MHz spectrometer at room temperature, with DMSO-d6 or CDCl3 as solvent. In order to promote the dissolution of the PCL25-b-PTrp2-b-P(Lys13-stat-Phe4), a drop of CF3COOD was added to break the hydrogen bonding in polypeptides.
The DLS studies of aqueous polypeptide-based vesicle dispersion were conducted for four times using a ZETASIZER Nano series instrument (Malvern Instruments ZS 90) at a scattering angle of 90°. Disposable cuvettes were used to analyze the aqueous vesicle dispersion. The data were processed by cumulative analysis of the experimental correlation function. The diameters of the vesicles were calculated from the computed diffusion coefficients using the Stokes-Einstein equation.
TEM images were taken by a JEOL JEM-2100F instrument at 200 kV equipped with a Gatan 894 Ultrascan 1000 CCD camera. Vesicle dispersion (5.0 μL) was dropped on the carbon-coated copper grid and dried at ambient environment for 12 h. A neutral phosphotungstic acid solution (1%, pH=7) was used to stain the copper grid for 1 min.
The zeta potential study of aqueous vesicle dispersion was determined using Nano-ZS 90 Nanosizer (Malvern Instruments Ltd., Worcestershire, U.K.) at a fixed scattering angle of 90°.
The critical vesiculation concentration of the vesicles is defined as the lowest concentration of polymers to self-assemble into vesicles in water. Pyrene (2.0 mg) was dissolved in acetone (12.5 mL). Then, the solution (10.0 μL) was added into the centrifuge tubes and dried overnight. The vesicle dispersion was diluted with deionized water to a range of concentrations (2000 μg/mL to 16.0 μg/mL) and added into centrifuge tubes respectively. The vesicle dispersion was stirred overnight. Fluorescence intensity of each sample was measured at 334 nm via a Lumina Fluorescence Spectrometer (Thermo Fisher). The intensity of I1 (373 nm) was chosen as the vibronic bands. The intensity values against the common logarithm (log) of the concentration of each sample were divided into two groups and processed by the same linear fit. Finally, the two lines intersected at one point, and the log of concentration at this point is the CVC of the vesicles.
Antibacterial Tests against Planktonic Bacteria
Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)
The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of the antibacterial polypeptide-based vesicles was determined by the broth microdilution assay.[43] E. coli and S. aureus were cultivated in the LB medium (0.100 g/mL) in an oven at 37 °C for 12 h. The bacterial suspension (10.0 μL) was added into the LB medium (10.0 mL) to make the diluted bacteria suspension. The vesicle dispersion was diluted with the LB broth to a range of concentrations (2000 μg/mL to 16.0 μg/mL). The diluted vesicle dispersions (100 μL) were placed on the 96-well culture plate. Then LB medium (100.0 μL) containing diluted bacteria was mixed with the diluted vesicle dispersion on the 96-well culture plate. The LB medium (100.0 μL) containing bacteria without vesicle dispersion was used as control. The 96-well plate was cultured in a shaking bed at 37 °C for 24 h. The MIC value was obtained by observing the growth of bacteria with the naked eye. All the results were obtained from independent experiments repeated for three times.
Dynamic antibacterial experiment
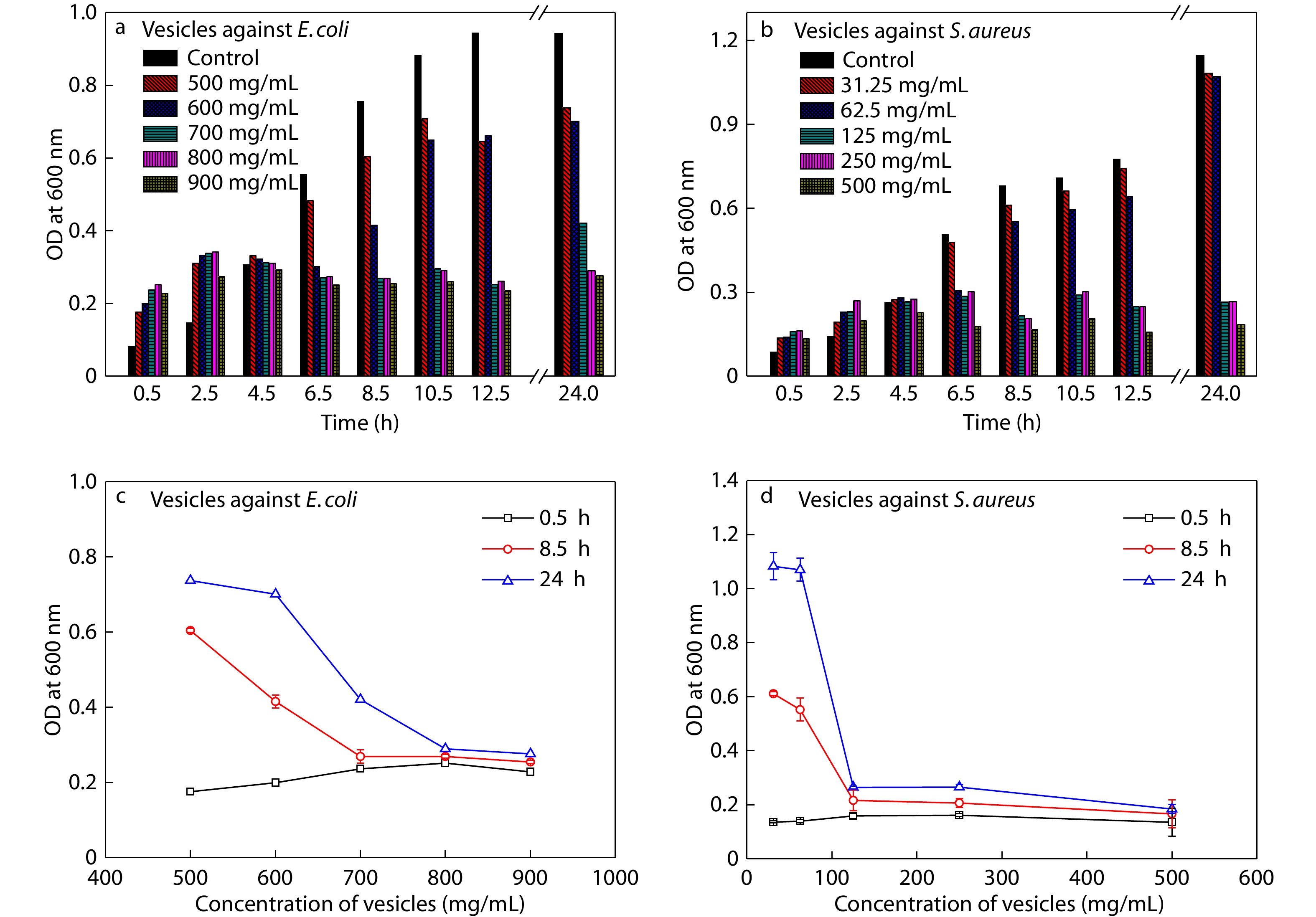
The diluted bacteria suspension was prepared as described above.[43] The diluted bacteria suspensions (180.0 μL) were placed on the 96-well culture plate. Then vesicle dispersion was diluted to a range of concentrations (0.2 mL, 1000.0 μg/mL to 50.0 μg/mL) and added into the 96-well culture plate. The 96-well plate was cultured in a shaking bed at 37 °C. Water (0.2 mL) was added into the 96-well culture plate used as control. The optical density (OD) of the mixed suspension was measured at 600 nm of wavelength at intervals during incubation. All the results were obtained from independent experiments repeated for three times.
Minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC)
The minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) was determined by standard plate counting method.[43] The mixed suspension in the clear well of the 96-well plate in the above experiment was diluted for 10 times, 100 times and 1000 times with PBS, respectively. The same operation was performed in the control group. The LB agar (10.0 mL, 0.100 g/mL) and the diluted mixed suspension (100.0 μL) were added into the culture plate. The culture plates were shaken gently to mix the suspension well. Then culture plates were cultured in 37 °C for 48 h. The MBC value was obtained by observing the growth of bacteria with the naked eye. All the results were obtained from independent experiments repeated for three times.
Visualization of Antibacterial Process
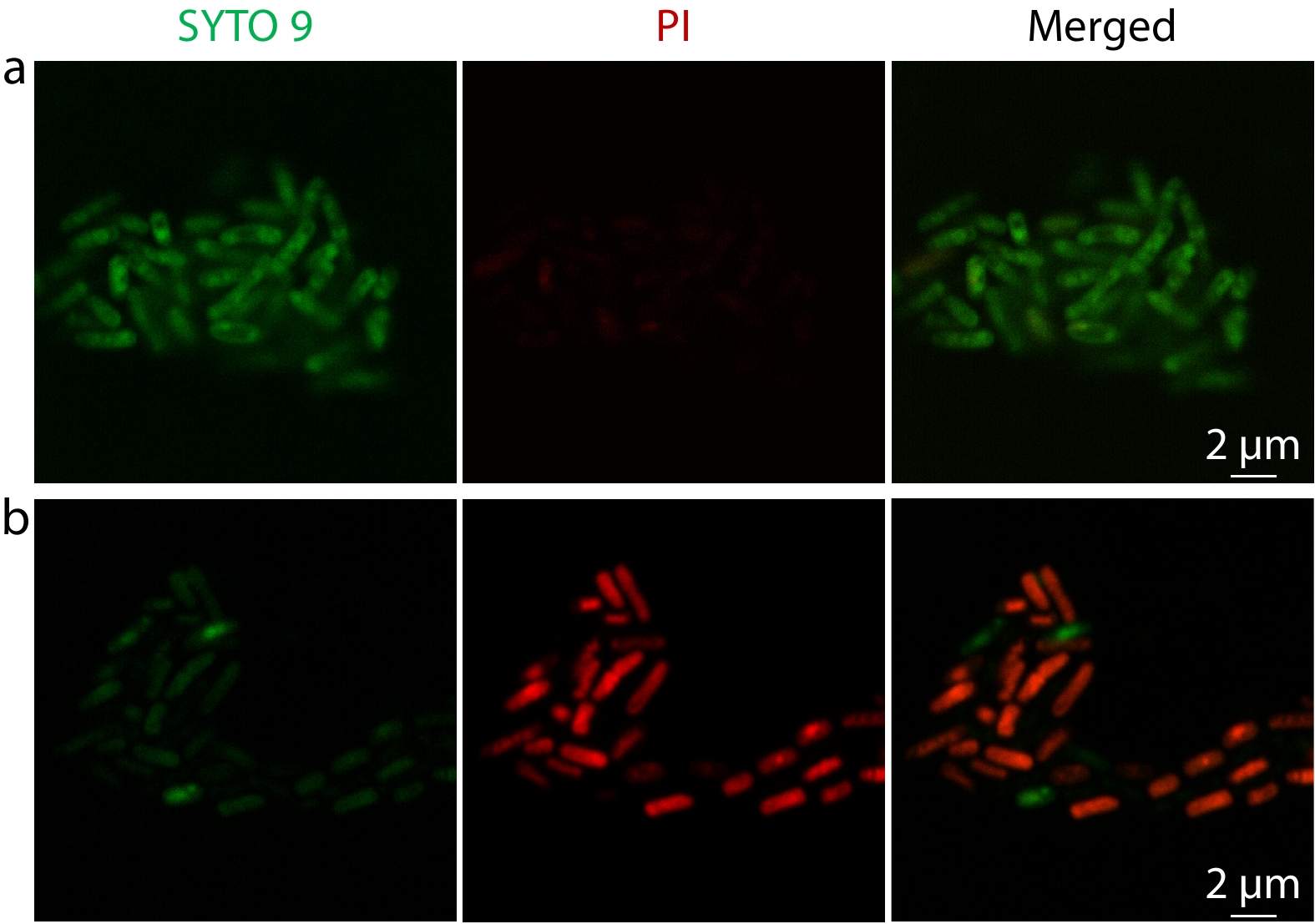
Method I. 300 μL of bacteria suspension (E. coli, ~109 colony-forming units (CFU)/mL) was added to 1.0 mL of vesicle dispersion (5.0 mg/mL), and incubated together in a shaking bed at 37 °C for 0 h, 1 h and 4 h. Then, the mixture dispersion was centrifugated at 6000 r/min for 15 min and resuspended in 300 μL of PBS containing 0.5 μL of SYTO 9 dye solution and 0.5 μL of propidium iodide solution (L7012 live/dead BacLight, Thermo Fisher Scientific) for 15 min in the dark at 37 °C after removing the supernatant. Centrifugation was performed again at 6000 r/min and resuspended the deposit in 100.0 μL of PBS to obtain the dyed sample. The rest operations are the same as above.
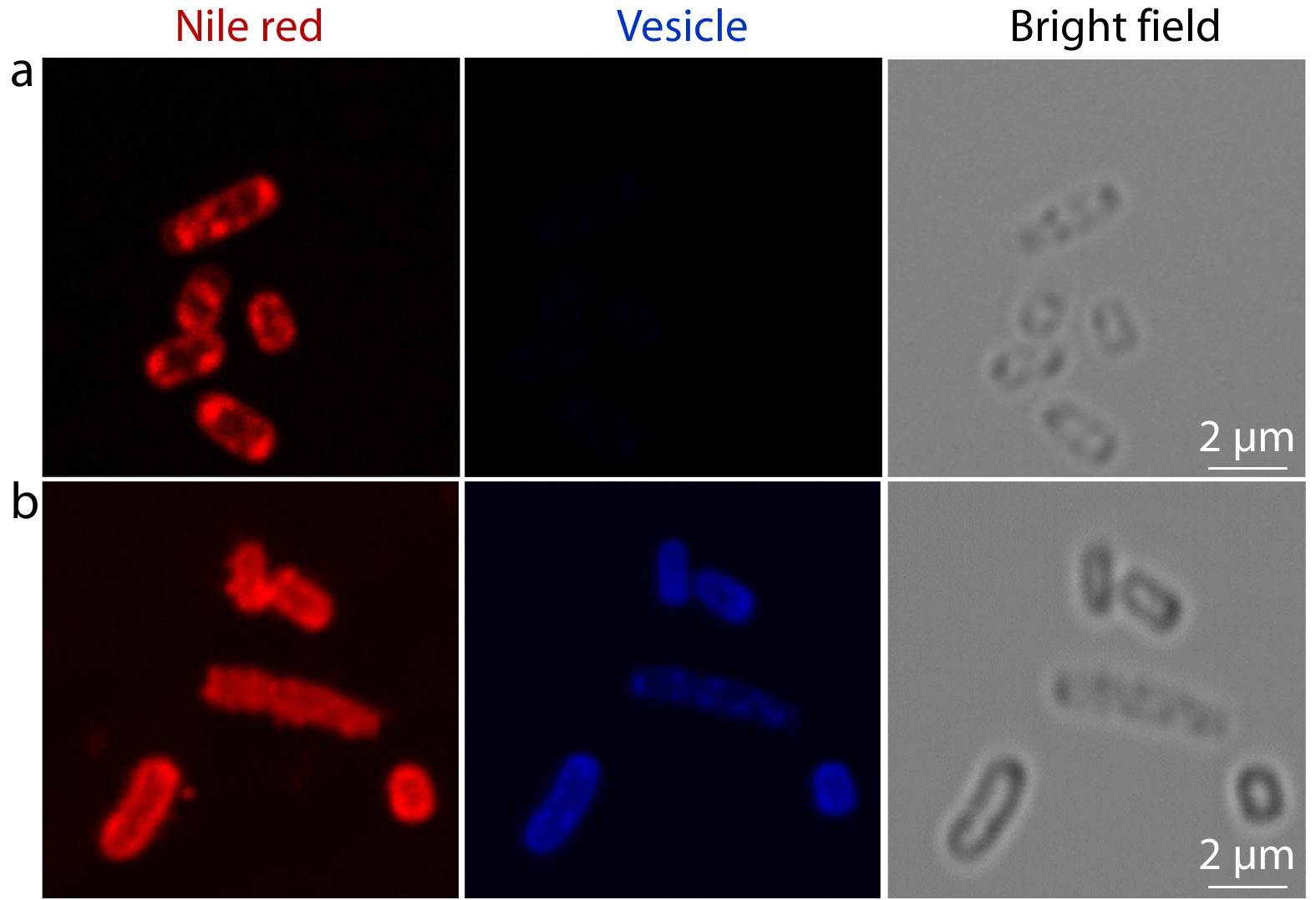
Method II. The breakage of bacterial membrane under the treatment of vesicles was revealed by Confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). 200 μL of bacteria suspension (E. coli, ~109 colony-forming units (CFU)/mL) was added to 1.0 mL of vesicle dispersion (5.0 mg/mL), and incubated together in a shaking bed at 37 °C for 0 h and 4 h, respectively. Then, the mixture dispersion was centrifugated at 6000 r/min for 15 min and resuspended in 1.0 mL of PBS after removing the supernatant. 1.0 μL of Nile red (2.0 mg/mL in acetone) was added to this culture to stain the bacterial membranes. Subsequently, 1.0 μL of the dispersion mentioned above was dropped on a clean glass slide and covered with a circle cover slip. After sealing the edge of slides with moderate nail polish, the samples were observed under a 63×oil immersion objective of an inverted microscope.[57]
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Synthesis and Self-assembly of Copolymers
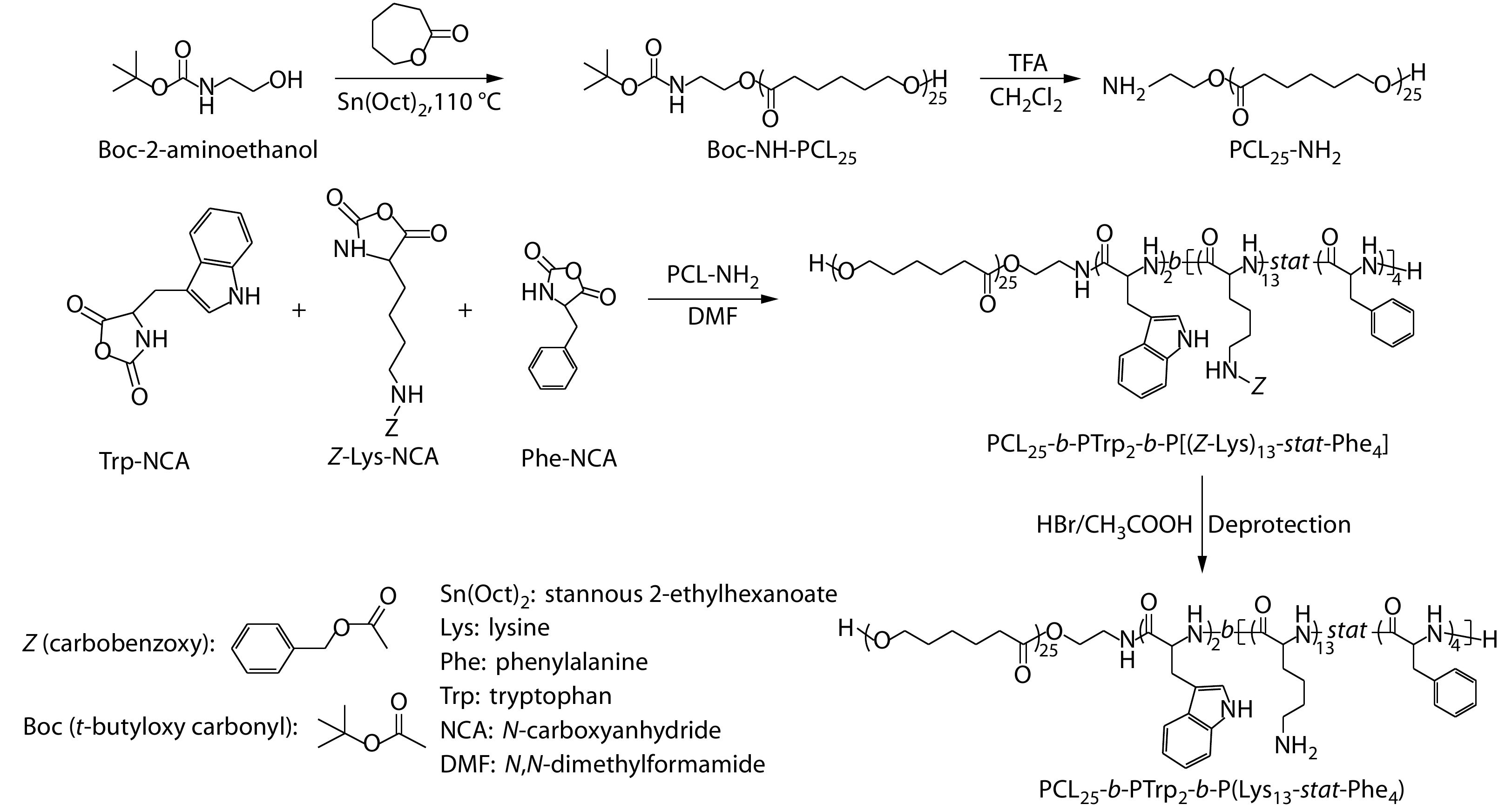
The antibacterial polypeptide-based polymer was synthesized by ring-opening polymerizations of PCL-NH2 and (Z)-Lys-N-carboxyanhydride (Z-Lys-NCA), Phe-NCA, and Trp-NCA monomers, as we previously reported.[58-60] The synthetic route is shown in Fig. 1. First, Z-Lys-NCA, Phe-NCA and Trp-NCA monomers were synthesized by NCA ring forming reaction. Second, N-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-2-aminoethanol initiated ring-opening polymerization of ε-caprolactone under the catalysis of stannous 2-ethylhexanoate (Sn(Oct)2) to afford PCL-NH-Boc. Third, PCL-NH-Boc was deprotected in the presence of TFA to obtain PCL-NH2. Fourth, L-Trp-NCA was dissolved with a DMF solution of PCL-NH2 for ring-opening polymerization to afford PCL-b-PTrp. After purification, PCL-b-PTrp, Z-Lys-NCA and Phe-NCA were dissolved in DMF for ring-opening polymerization to afford PCL-b-PTrp-b-P[(Z-Lys)-stat-Phe]. Finally, lysine units were deprotected and purified to obtain PCL-b-PTrp-b-P(Lys-stat-Phe). The proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H-NMR) spectra and size exclusion chromatography (SEC) results are provided in Figs. S2−S10 in ESI which validated the successful synthesis of the polypeptide-based polymers.
Preparation of Polypeptide-based Vesicles
The antibacterial polymer was self-assembled into vesicles in the mixture of DMF/H2O (1/3, V/V) by solvent switch method.[61-63] The dispersion was transferred into a dialysis tube and dialyzed to remove DMF. Finally, the PCL block and Trp block form the membrane of the vesicle and partially hydrophilic moieties and Lys block form the corona of the vesicle.
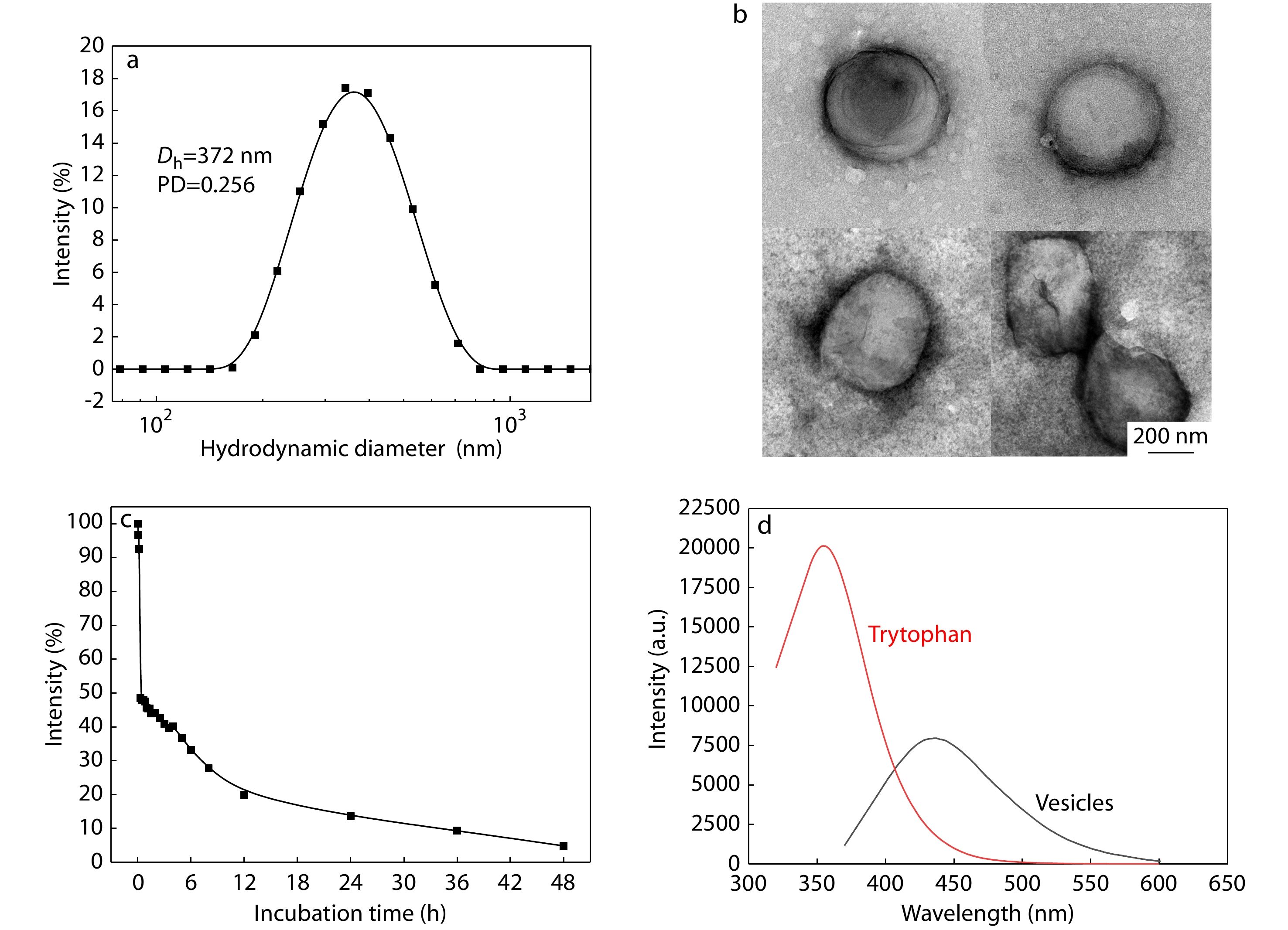
To study the physicochemical properties of the vesicles, dynamic light scattering (DLS), TEM and fluorescence spectrometer were utilized. DLS results (Fig. 2a) revealed that the vesicles have a Z-averaged hydrodynamic diameter of about 372 nm with a polydispersity index (PDI) of 0.256. TEM images (Fig. 2b) indicated that the assemblies have a hollow spherical structure with a number-averaged diameter of about 400 nm, which is consistent with the results of DLS analysis. As shown in Fig. S11 in ESI, the CVC of the synthesized polymer is 30.1 μg/mL. Besides, the biodegradation of the vesicles was studied using trypsin (Fig. 2c), indicating that over 50% of vesicles were degraded within 2 h in the presence of 800 μg/mL of trypsin and more than 95% of vesicles were degraded after 48 h. In addition, the fluorescence property of vesicles was studied. After polymerization and self-assembly, the emission maximum was shifted from 354 nm of tryptophan in the ultraviolet range to 436 nm in the visible range (Fig. 2d). Such fluorescence red shift could be attributed to the delocalization of related electrons within the hydrogen binds within and between the polypeptides.
Visualization of Antibacterial Process
E. coli (ATCC35218) and S. aureus (ATCC29213) were used to represent Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria for visualization of antibacterial process, respectively.[38,64,65] In order to verify the antibacterial property of vesicles, MIC (minimum inhibitory concentration) and MBC (minimum bactericidal concentration) values were determined by means of 96-well plate method and plate counting method (Table S1 and Fig. S12 in ESI). Also, in order to verify the dynamic antibacterial activity of vesicles, the optical densities of bacterial suspension with and without treatment were analyzed (Figs. 3a−3d). Meanwhile, the CVC of PCL25-b-PTrp2-b-P(Lys13-stat-Phe4) is lower than the MIC values, indicating that the growth of bacteria was inhibited by vesicles, rather than polypeptides alone.
Furthermore, LIVE/DEADTM BacLightTM Bacterial Viability Kit was used to visually assess the antibacterial activity of vesicles (Fig. 4). Live bacteria with an intact membrane were stained green whereas dead bacteria with a compromised membrane were stained red. Nearly all the bacteria were alive at the beginning (Fig. 4a) before treated with vesicles. While after 4 h of vesicle treatment, most of them went dead with clear red fluorescence (Fig. 4b), validating the antibacterial activity of vesicles against planktonic bacteria.
Utilizing the intrinsic blue fluorescence of polypeptide based vesicles, real-time fluorescence imaging was conducted to study the changes of bacterial membranes during antibacterial process (Fig. 5). To obtain a clear visualization of bacterial membrane, Nile red was applied as a lipophilic cell membrane stain.[57] Before treatment with polypeptide-based vesicles, clear and intact bacterial membrane with red fluorescence was observed under CLSM (Fig. 5a). At the same time, no blue fluorescence was captured from bacteria alone (Fig. 5a). Meanwhile, after treated with polypeptide-based vesicles for 4 h, both blue and red fluorescences were observed from bacteria (Fig. 5b). It is noteworthy that the blue fluorescence from vesicles was captured from both bacterial membrane and cytoplasm, indicating selective targeting capability of vesicles towards bacteria. It can be attributed to electrostatic interactions between positively-charged vesicles (zeta potential at +56 mV) and negatively-charged bacterial membrane. Also, discontinued and aggregated red fluorescence was observed from the bacterial membrane (Fig. 5b). Such discontinuity of bacterial membrane could be ascribed to the phenyl groups of phenylalanine and tryptophan piercing into the bacteria membrane, which destroyed the membrane integrity.
CONCLUSIONS
In summary, we have developed a polypeptide-based vesicle that possesses visible blue fluorescence without introducing any fluorophore for visualization of antibacterial process. Through modular design to integrate multiple functional fragments, PCL25-b-PTrp2-b-P(Lys13-stat-Phe4) copolymer was synthesized, where PCL chains form the hydrophobic membrane, P(Lys-stat-Phe) and PTrp provide intrinsic fluorescence and broad-spectrum antibacterial activity. Meanwhile, after polymerization and self-assembly, the fluorescence emission was shifted from invisible ultraviolet range of amino acids to visible range (emission maximum at 436 nm), which offers an opportunity for real-time monitoring the interaction between polypeptide-based vesicles and bacteria. Moreover, through utilizing the intrinsic fluorescence of vesicles, confocal fluorescence imaging of vesicles with bacteria validated the specific adhesion of vesicle towards bacteria and the bacterial death through membrane disruption. Overall, we have developed a new class of biodegradable polypeptide-based vesicles with intrinsic fluorescence for visualization of antibacterial process, which could be a promising imaging approach in biomedical research field.
Polymers for bioimaging
Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007 32 1031 1053Kim, J. H.; Park, K.; Nam, H. Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I. C. Polymers for bioimaging. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 1031−1053.
Development of fluorescent probes for bioimaging applications
P. Jpn. Acad. B-Phys. 2010 86 837 847Nagano, T. Development of fluorescent probes for bioimaging applications. P. Jpn. Acad. B-Phys. 2010, 86, 837−847.
Nano-sized MRI contrast agents with dendrimer cores
Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2005 57 2271 2286Kobayashi, H.; Brechbiel, M. W. Nano-sized MRI contrast agents with dendrimer cores. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2005, 57, 2271−2286.
Application of high-resolution magic-angle spinning NMR spectroscopy to define the cell uptake of MRI contrast agents
J. Magn. Reson. 2002 156 222 229Calabi, L.; Alfieri, G.; Biondi, L.; De Miranda, M.; Paleari, L.; Ghelli, S. Application of high-resolution magic-angle spinning NMR spectroscopy to define the cell uptake of MRI contrast agents. J. Magn. Reson. 2002, 156, 222−229.
Controllable emission via tuning the size of fluorescent nano-probes formed by polymeric amphiphiles
Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2019 37 767 773Wang, X. C.; Zhou, S. X.; Ding, L.; Zhao, Y. H.; Min, S. X.; Dong, B.; Song, B. Controllable emission via tuning the size of fluorescent nano-probes formed by polymeric amphiphiles. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2019, 37, 767−773.
NIR emission nanoparticles based on FRET composed of AIE luminogens and NIR dyes for two-photon fluorescence imaging
Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2019 37 401 408Liu, L. J.; Liu, W.; Ji, G.; Wu, Z. Y.; Xu, B.; Qian, J.; Tian, W. J. NIR emission nanoparticles based on FRET composed of AIE luminogens and NIR dyes for two-photon fluorescence imaging. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2019, 37, 401−408.
Multi-mode full spectrum dark field microscope for single nanoparticle localized surface plasmon resonance dynamics study
Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. (in Chinese) 2019 35 371 377Liu, L.; Hao, Y.; Deng, S.; Wang, K.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Fan, C.; Li, J.; Liu, H. Multi-mode full spectrum dark field microscope for single nanoparticle localized surface plasmon resonance dynamics study. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. (in Chinese) 2019, 35, 371−377.
Modern imaging technologies in toxicologic pathology: an overview
Toxicol. Pathol. 2006 34 815 826Ying, X.; Monticello, T. M. Modern imaging technologies in toxicologic pathology: an overview. Toxicol. Pathol. 2006, 34, 815−826.
Automatic quantitation of localized in vivo H-1 spectra with LCModel
NMR Biomed. 2001 14 260 264Provencher, S. W. Automatic quantitation of localized in vivo H-1 spectra with LCModel. NMR Biomed. 2001, 14, 260−264.
In vivo magnetic resonance detection of cancer by using multifunctional magnetic nanocrystals
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005 127 12387 12391Huh, Y. M.; Jun, Y. W.; Song, H. T.; Kim, S.; Choi, J. S.; Lee, J. H.; Yoon, S.; Kim, K. S.; Shin, J. S.; Suh, J. S.; Cheon, J. In vivo magnetic resonance detection of cancer by using multifunctional magnetic nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12387−12391.
Review of advanced imaging techniques
J. Pathol. Inform. 2012 3 22 22Chen, Y.; Liang, C. P.; Liu, Y.; Fischer, A. H.; Parwani, A. V.; Pantanowitz, L. Review of advanced imaging techniques. J. Pathol. Inform. 2012, 3, 22−22.
Aptamer-conjugated nanomaterials for specific cancer diagnosis and targeted therapy
Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. (in Chinese) 2018 34 348 360Bai, H.; Fan, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Tan, W. Aptamer-conjugated nanomaterials for specific cancer diagnosis and targeted therapy. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. (in Chinese) 2018, 34, 348−360.
Aggregation-induced emission probe for study of the bactericidal mechanism of antimicrobial peptides
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018 10 11436 11442Chen, J.; Gao, M.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; He, J.; Qin, A.; Ren, L.; Wang, Y.; Tang, B. Z. Aggregation-induced emission probe for study of the bactericidal mechanism of antimicrobial peptides. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 11436−11442.
Antibacterial activity and mechanism of cinnamon essential oil against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus
Food Control 2016 59 282 289Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, P.; Quek, S. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of cinnamon essential oil against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Food Control 2016, 59, 282−289.
Synthetic cationic amphiphilic α-helical peptides as antimicrobial agents
Biomaterials 2011 32 2204 2212Wiradharma, N.; Khoe, U.; Hauser, C. A. E.; Seow, S. V.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y. Y. Synthetic cationic amphiphilic α-helical peptides as antimicrobial agents. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 2204−2212.
Surface antimicrobial activity and biocompatibility of incorporated polyethylenimine nanoparticles
Biomaterials 2008 29 4157 4163Beyth, N.; Houri-Haddad, Y.; Baraness-Hadar, L.; Yudovin-Farber, I.; Domb, A. J.; Weiss, E. I. Surface antimicrobial activity and biocompatibility of incorporated polyethylenimine nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4157−4163.
Atomic force microscopy study of the effect of antimicrobial peptides on the cell envelope of Escherichia coli
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005 49 4085 4092Meincken, A.; Holroyd, D. L.; Rautenbach, M. Atomic force microscopy study of the effect of antimicrobial peptides on the cell envelope of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 4085−4092.
AFM studies of inhibition effect in binding of antimicrobial peptide and immune proteins
Langmuir 2007 23 10438 10440Kim, J. S.; Jang, S.; Kim, U.; Cho, K. AFM studies of inhibition effect in binding of antimicrobial peptide and immune proteins. Langmuir 2007, 23, 10438−10440.
Atomic force microscopy study of the antimicrobial action of Sushi peptides on Gram negative bacteria
Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2007 1768 411 418Li, A.; Lee, P. Y.; Ho, B.; Ding, J. L.; Lim, C. T. Atomic force microscopy study of the antimicrobial action of Sushi peptides on Gram negative bacteria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2007, 1768, 411−418.
Imaging bacterial cell death induced by antimicrobial peptides in real time using high speed AFM
Microsc. Microanal. 2010 16 466 467Fantner, G. E.; Barbero, R. J.; Gray, D. S.; Belcher, A. M. Imaging bacterial cell death induced by antimicrobial peptides in real time using high speed AFM. Microsc. Microanal. 2010, 16, 466−467.
Synthesis and mechanism insight of a peptide-grafted hyperbranched polymer nanosheet with weak positive charges but excellent intrinsically antibacterial efficacy
Biomacromolecules 2016 17 2080 2086Gao, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, F.; Du, J. Synthesis and mechanism insight of a peptide-grafted hyperbranched polymer nanosheet with weak positive charges but excellent intrinsically antibacterial efficacy. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 2080−2086.
Damage of the bacterial cell envelope by antimicrobial peptides gramicidin S and PGLA as revealed by transmission and scanning electron microscopy
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010 54 3132 3142Hartmann, M.; Berditsch, M.; Hawecker, J.; Ardakani, M. F.; Gerthsen, D.; Ulrich, A. S. Damage of the bacterial cell envelope by antimicrobial peptides gramicidin S and PGLA as revealed by transmission and scanning electron microscopy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3132−3142.
Antibacterial activity and mechanism of silver nanoparticles on Escherichia coli
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010 85 1115 1122Li, W. R.; Xie, X. B.; Shi, Q. S.; Zeng, H. Y.; Ou-Yang, Y. S.; Chen, Y. B. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of silver nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1115−1122.
The morphological effects of 2 antimicrobial peptides, hecate-1 and melittin, on Escherichia-coli
Scanning Microsc. 1995 9 501 507Henk, W. G.; Todd, W. J.; Enright, F. M.; Mitchell, P. S. The morphological effects of 2 antimicrobial peptides, hecate-1 and melittin, on Escherichia-coli. Scanning Microsc. 1995, 9, 501−507.
Construction and applications of well-defined porphyrin-containing polymers
Acta Polymerica Sinica (in Chinese) 2019 50 653 670Tian, J.; Zhang, W. A. Construction and applications of well-defined porphyrin-containing polymers. Acta Polymerica Sinica (in Chinese) 2019, 50, 653−670.
Rapid and reliable detection of antimicrobial peptide penetration into gram-negative bacteria based on fluorescence quenching
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009 53 3501 3504Benincasa, M.; Pacor, S.; Gennaro, R.; Scocchi, M. Rapid and reliable detection of antimicrobial peptide penetration into gram-negative bacteria based on fluorescence quenching. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 3501−3504.
Stability enhancement of fluorophores for lighting up practical application in bioimaging
Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015 44 4179 4184Wu, X.; Zhu, W. Stability enhancement of fluorophores for lighting up practical application in bioimaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4179−4184.
Photophysical processes in single molecule organic fluorescent probes
Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014 43 1057 1075Stennett, E. M. S.; Ciuba, M. A.; Levitus, M. Photophysical processes in single molecule organic fluorescent probes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 1057−1075.
Polyion complex stability and gene silencing efficiency with a siRNA-grafted polymer delivery system
Biomaterials 2010 31 8097 8105Takemoto, H.; Ishii, A.; Miyata, K.; Nakanishi, M.; Oba, M.; Ishii, T.; Yamasaki, Y.; Nishiyama, N.; Kataoka, K. Polyion complex stability and gene silencing efficiency with a siRNA-grafted polymer delivery system. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 8097−8105.
Mimicking the cell membrane with block copolymer membranes
J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 2012 50 2293 2318Zhang, X.; Tanner, P.; Graff, A.; Palivan, C. G.; Meier, W. Mimicking the cell membrane with block copolymer membranes. J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 2012, 50, 2293−2318.
Multifunctional polymer vesicles for ultrasensitive magnetic resonance imaging and drug delivery
J. Mater. Chem. 2012 22 12329 12338Ren, T.; Liu, Q.; Lu, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Du, J. Multifunctional polymer vesicles for ultrasensitive magnetic resonance imaging and drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 12329−12338.
Hydrophobic modifications of cationic polymers for gene delivery
Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010 35 1144 1162Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, C.; Jiao, Y. Hydrophobic modifications of cationic polymers for gene delivery. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 1144−1162.
pH-Sensitive block copolymer vesicles with variable trigger points for drug delivery
Macromolecules 2012 45 8275 8283Du, J.; Fan, L.; Liu, Q. pH-Sensitive block copolymer vesicles with variable trigger points for drug delivery. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 8275−8283.
Polymer vesicles: Mechanism, preparation, application, and responsive behavior
Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017 64 1 22Zhu, Y.; Yang, B.; Chen, S.; Du, J. Polymer vesicles: Mechanism, preparation, application, and responsive behavior. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 64, 1−22.
Cooperative modulation of bilayer permeability and microstructures of polymersomes
Acta Polymerica Sinica (in Chinese) 2019 50 553 566Yao, C. Z.; Wang, X. R.; Hu, J. M.; Liu, S. Y. Cooperative modulation of bilayer permeability and microstructures of polymersomes. Acta Polymerica Sinica (in Chinese) 2019, 50, 553−566.
Ultrasound-responsive homopolymer nanoparticles
Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2020 38 349 356Yang, B.; Du, J. Ultrasound-responsive homopolymer nanoparticles. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 38, 349−356.
Co-delivery of doxorubicin and afatinib with ph-responsive polymeric nanovesicle for enhanced lung cancer therapy
Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2019 37 1224 1233Gong, H. Y.; Chen, Y. G.; Yu, X. S.; Xiao, H.; Xiao, J. P.; Wang, Y.; Shuai, X. T. Co-delivery of doxorubicin and afatinib with ph-responsive polymeric nanovesicle for enhanced lung cancer therapy. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2019, 37, 1224−1233.
Recent progress in fluorescent vesicles with aggregation-induced emission
Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2019 37 352 371Chen, H.; Li, M. H. Recent progress in fluorescent vesicles with aggregation-induced emission. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2019, 37, 352−371.
Multifunctional homopolymer vesicles for facile immobilization of gold nanoparticles and effective water remediation
ACS Nano 2014 8 5022 5031Zhu, Y.; Fan, L.; Yang, B.; Du, J. Multifunctional homopolymer vesicles for facile immobilization of gold nanoparticles and effective water remediation. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5022−5031.
Charged polypeptide vesicles with controllable diameter
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005 127 12423 12428Holowka, E. P.; Pochan, D. J.; Deming, T. J. Charged polypeptide vesicles with controllable diameter. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12423−12428.
Encapsulation of myoglobin in PEGylated polyion complex vesicles made from a pair of oppositely charged block lonomers: A physiologically available oxygen carrier
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007 46 6085 6088Kishimura, A.; Koide, A.; Osada, K.; Yamasaki, Y.; Kataoka, K. Encapsulation of myoglobin in PEGylated polyion complex vesicles made from a pair of oppositely charged block lonomers: A physiologically available oxygen carrier. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 6085−6088.
Doxorubicin loaded magnetic polymersomes: theranostic nanocarriers for MR Imaging and Magneto-Chemotherapy
ACS Nano 2011 5 1122 1140Sanson, C.; Diou, O.; Thevenot, J.; Ibarboure, E.; Soum, A.; Brulet, A.; Miraux, S.; Thiaudiere, E.; Tan, S.; Brisson, A.; Dupuis, V.; Sandre, O.; Lecommandoux, S. Doxorubicin loaded magnetic polymersomes: theranostic nanocarriers for MR Imaging and Magneto-Chemotherapy. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1122−1140.
Dual corona vesicles with intrinsic antibacterial and enhanced antibiotic delivery capabilities for effective treatment of biofilm-induced periodontitis
ACS Nano 2019 13 13645 13657Xi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Xiao, Y.; Du, J. Dual corona vesicles with intrinsic antibacterial and enhanced antibiotic delivery capabilities for effective treatment of biofilm-induced periodontitis. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 13645−13657.
Highly effective antibacterial vesicles based on peptide-mimetic alternating copolymers for bone
Biomacromolecules 2017 18 4154 4162Zhou, C.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, P.; Wang, F.; Hong, Y.; Wang, N.; Xu, S.; Du, J. Highly effective antibacterial vesicles based on peptide-mimetic alternating copolymers for bone. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 4154−4162.
Antibacterial polymeric nanostructures for biomedical applications
Chem. Commun. 2014 50 14482 14493Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Liu, Q.; Du, J. Antibacterial polymeric nanostructures for biomedical applications. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 14482−14493.
Antibacterial high-genus polymer vesicle as an "armed" drug carrier
J. Mater. Chem. B 2013 1 5496 5504Zhu, H.; Geng, Q.; Chen, W.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, J.; Du, J. Antibacterial high-genus polymer vesicle as an "armed" drug carrier. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 5496−5504.
Antibacterial vesicles by direct dissolution of a block copolymer in water
Polym. Chem. 2013 4 255 259Zhang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Yuan, W.; Du, J. Antibacterial vesicles by direct dissolution of a block copolymer in water. Polym. Chem. 2013, 4, 255−259.
Water-dispersible and biodegradable polymer micelles with good antibacterial efficacy
Chem. Commun. 2012 48 6857 6859Yuan, W.; Wei, J.; Lu, H.; Fan, L.; Du, J. Water-dispersible and biodegradable polymer micelles with good antibacterial efficacy. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 6857−6859.
Fluorescence monitoring of peptide transport pathways into large and giant vesicles by supramolecular host-dye reporter pairs
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019 141 20137 20145Barba-Bon, A.; Pan, Y. C.; Biedermann, F.; Guo, D. S.; Nau, W. M.; Hennig, A. Fluorescence monitoring of peptide transport pathways into large and giant vesicles by supramolecular host-dye reporter pairs. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 20137−20145.
Organic dyes for deep bioimaging
Nature 2017 551 176 177Schnermann, M. J. Organic dyes for deep bioimaging. Nature 2017, 551, 176−177.
Dye-protein hybrid nanoparticles for photothermal therapy of tumor cells
Acta Polymerica Sinica (in Chinese) 2019 50 633 641Zhang, J. X.; Sun, T. T.; Xie, Z. G. Dye-protein hybrid nanoparticles for photothermal therapy of tumor cells. Acta Polymerica Sinica (in Chinese) 2019, 50, 633−641.
IR-780 dye loaded tumor targeting theranostic nanoparticles for NIR imaging and photothermal therapy
Biomaterials 2013 34 6853 6861Yue, C.; Liu, P.; Zheng, M.; Zhao, P.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Cai, L. IR-780 dye loaded tumor targeting theranostic nanoparticles for NIR imaging and photothermal therapy. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 6853−6861.
Multimodal image-guided photothermal therapy mediated by re-188-labeled micelles containing a cyanine-type photosensitizer
ACS Nano 2011 5 5594 5607Peng, C. L.; Shih, Y. H.; Lee, P. C.; Hsieh, T. M. H.; Luo, T. Y.; Shieh, M. J. Multimodal image-guided photothermal therapy mediated by re-188-labeled micelles containing a cyanine-type photosensitizer. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 5594−5607.
Prevalent intrinsic emission from nonaromatic amino acids and poly(amino acids)
Sci. China-Chem. 2018 61 351 359Chen, X.; Luo, W.; Ma, H.; Peng, Q.; Yuan, W. Z.; Zhang, Y. Prevalent intrinsic emission from nonaromatic amino acids and poly(amino acids). Sci. China-Chem. 2018, 61, 351−359.
A label-free, quantitative assay of amyloid fibril growth based on intrinsic fluorescence
ChemBioChem 2013 14 846 850Pinotsi, D.; Buell, A. K.; Dobson, C. M.; Schierle, G. S. K.; Kaminski, C. F. A label-free, quantitative assay of amyloid fibril growth based on intrinsic fluorescence. ChemBioChem 2013, 14, 846−850.
Clustering-triggered emission of nonconjugated polyacrylonitrile
Small 2016 12 6586 6592Zhou, Q.; Cao, B.; Zhu, C.; Xu, S.; Gong, Y.; Yuan, W. Z.; Zhang, Y. Clustering-triggered emission of nonconjugated polyacrylonitrile. Small 2016, 12, 6586−6592.
Omega 76: a designed antimicrobial peptide to combat carbapenem and tigecycline-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
Sci. Adv. 2019 5 eaax1946Nagarajan, D.; Roy, N.; Kulkarni, O.; Nanajkar, N.; Datey, A.; Ravichandran, S.; Thakur, C.; Sandeep, T.; Aprameya, I. V.; Sarma, S. P.; Chakravortty, D.; Chandra, N. Omega 76: a designed antimicrobial peptide to combat carbapenem and tigecycline-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax1946.
Polymersome-hydrogel composites with combined quick and long-term antibacterial activities
J. Mater. Chem. B 2018 6 6311 6321Hong, Y.; Xi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Zhang, H.; Yan, N.; He, S.; Du, J. Polymersome-hydrogel composites with combined quick and long-term antibacterial activities. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 6311−6321.
Synthesis, self-assembly, and biomedical applications of antimicrobial peptide-polymer conjugates
Biomacromolecules 2018 19 1701 1720Sun, H.; Hong, Y.; Xi, Y.; Zou, Y.; Gao, J.; Du, J. Synthesis, self-assembly, and biomedical applications of antimicrobial peptide-polymer conjugates. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 1701−1720.
ε-Poly(L-lysine)-based hydrogels with fast-acting and prolonged antibacterial activities
Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2018 36 1239 1250Zou, Y. J.; He, S. S.; Du, J. Z. ε-Poly(L-lysine)-based hydrogels with fast-acting and prolonged antibacterial activities. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 36, 1239−1250.
EpCAM-antibody-labeled noncytotoxic polymer vesicles for cancer stem cells-targeted delivery of anticancer drug and siRNA
Biomacromolecules 2015 16 1695 1705Chen, J.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, J.; Du, J. EpCAM-antibody-labeled noncytotoxic polymer vesicles for cancer stem cells-targeted delivery of anticancer drug and siRNA. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 1695−1705.
Bone-targeting polymer vesicles for simultaneous imaging and effective malignant bone tumor treatment
Biomaterials 2021 269 120345 120345Zhou, X.; Yan, N.; Cornel, E. J.; Cai, H.; Xue, S.; Xi, H.; Fan, Z.; He, S.; Du, J. Bone-targeting polymer vesicles for simultaneous imaging and effective malignant bone tumor treatment. Biomaterials 2021, 269, 120345−120345.
Design principles, synthesis and biomedical applications of polymer vesicles with inhomogeneous membranes
J. Control. Rel. 2020 326 365 386Liu, D.; Sun, H.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, S.; Cornel, E. J.; Zhu, Y.; Du, J. Design principles, synthesis and biomedical applications of polymer vesicles with inhomogeneous membranes. J. Control. Rel. 2020, 326, 365−386.
Antibacterial and pH-responsive quaternized hydroxypropyl cellulose-g-poly(THF-co-epichlorohydrin) graft copolymer: synthesis, characterization and properties
Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2020 38 704 714Deng, J. R.; Zhao, C. L.; Wu, Y. X. Antibacterial and pH-responsive quaternized hydroxypropyl cellulose-g-poly(THF-co-epichlorohydrin) graft copolymer: synthesis, characterization and properties. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 38, 704−714.
Infusing high-density polyethylene with graphene-zinc oxide to produce antibacterial nanocomposites with improved properties
Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2020 38 898 907Yao, Y. L.; De Guzman, M. R.; Duan, H.; Gao, C.; Lin, X.; Wen, Y. H.; Du, J.; Lin, L.; Chen, J. C.; Wu, C. S.; Suen, M. C.; Sun, Y. L.; Hung, W. S.; Tsou, C. H. Infusing high-density polyethylene with graphene-zinc oxide to produce antibacterial nanocomposites with improved properties. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 38, 898−907.